What Is Elasticsearch? The Hidden Power Behind Search

Elasticsearch isn’t just another search engine—it’s a powerhouse for real-time data exploration. From lightning-fast search results to advanced analytics, this open-source tool is reshaping how businesses handle vast amounts of information. Whether potential visitors are trying to locate a blog article on a specific topic or scouring an eCommerce website for products, having an on-site search engine can be beneficial.
Most users are already accustomed to using search engines such as Google, which processes approximately 5.8 billion searches per day. They expect the websites they visit to offer a similar quality search experience.
eCommerce and enterprise companies include this search functionality on their websites through something known as Elasticsearch. But Elasticsearch is more than just a search engine.
In this article, we’ll provide some guidance on what Elasticsearch is, explain how it works, and some of its benefits.
Key takeaways
- Elasticsearch Enhances Search & UX: It provides fast, accurate search functionality for websites, improving user experience with features like typo correction, autocomplete, and faceted search.
- Powerful for eCommerce & Content Management: Helps streamline product catalogs, boost customer engagement, and optimize content marketing with real-time analytics and search reporting.
- High Performance & Scalability: Uses a distributed system for fast, reliable searches across large datasets, making it ideal for enterprises handling vast amounts of information.
- Integration with Core dna: When combined with Core dna’s digital experience platform, Elasticsearch creates a seamless, connected digital experience beyond just search functionality.
On this page:
What is Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch is an analytics and full-text search engine that provides search functionality for web applications, including blogs, eCommerce websites and more. It is distributed, open-source, built on Apache Lucene and written in Java.
Elasticsearch is also one component of a set of open-source tools known as the ELK Stack. The others in that stack are Logstash and Kibana, and together they combine to provide data ingestion, storage, enrichment, visualization and analysis of data.
What is Elasticsearch for?
Elasticsearch is used to query and analyze data of various types, both structured and unstructured. Unlike other search tools that rely on text searches, Elasticsearch provides fast search responses using the same technology powering Google’s search engine, called inverted indexing, and other best-in-class algorithms.
Elasticsearch provides high performance, distributed architecture, scalability and speed.
It analyzes billions of data points in seconds and can provide aggregations to explore trends and patterns within the data. This enables several use cases such as search functionality for applications, websites and enterprises, logging, infrastructure metrics, analytics and more.
How does Elasticsearch work?
In order to understand how Elasticsearch works, it’s essential to learn more about some of the key components and how it organizes data.
In Elasticsearch, data is stored as JSON documents and separated into fields similar to rows and columns in a database. A blog article or data log of job descriptions would be examples of documents.

Next, we have an index. An index is similar to a database and is a collection of documents with similar properties or characteristics. Elasticsearch stores that document and adds a reference that makes it searchable in an index.
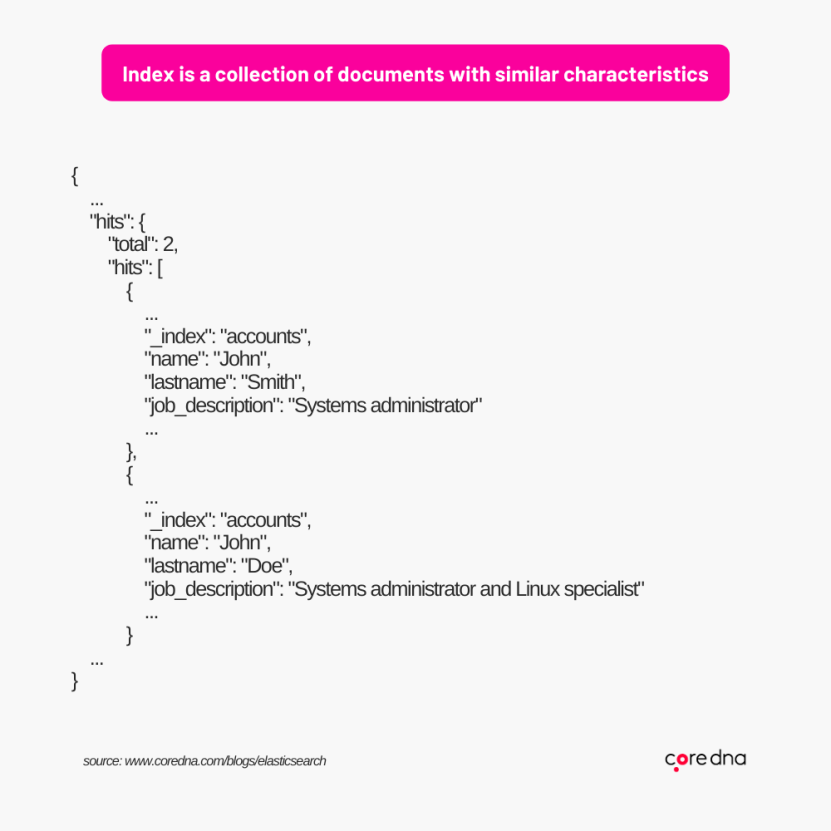
Data in an index isn’t stored directly in strings. Instead, documents are split into their individual search terms, and these terms are mapped to the documents.
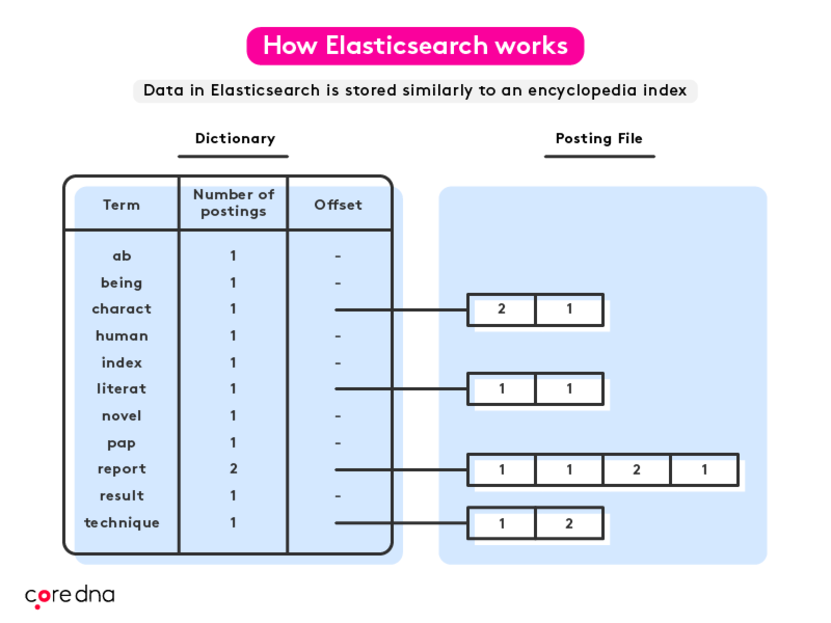
For example, when trying to find all of the times the word “human” is mentioned in an encyclopedia, you would have two options. Scan the entire book or turn to the index at the back that catalogs all of the words mentioned. Data in Elasticsearch is stored similarly to an encyclopedia index, allowing Elasticsearch to quickly find best-matches even when scanning large data sets.
General benefits of Elasticsearch
Search functionality is essential, but what makes Elasticsearch so popular within the enterprise? Here are a few of the general benefits.
1. Optimizes the user experience (UX)
Elasticsearch makes it possible for anyone to sift through large volumes of data quite easily. Not only can this data be searched, but Elasticsearch also organizes and filters that information to give it context.
It also provides a structure that pulls disparate data sources into one view. For example, when searching on an eCommerce website, Elasticsearch can push products with the most popularity or a five-star rating towards the top of the search results.
2. Enhances visitor engagement
Keeping visitors engaged can make the difference in converting them from simply a visitor and turning them into a customer. Elasticsearch can help visitors to find things they’re searching for faster than if they’re merely browsing.
Built-in features also allow it to correct typos, rectify spelling mistakes, and even autocomplete searches that customers may have been conducting.
3. Search result reporting
Search results or reports in Elasticsearch are boosted by the fact that different sorting and weighting methods can be introduced. It also facilitates advanced querying that enables users to retrieve a combination of queries and return more precise results from search.
Advanced search functionality, especially on busy eCommerce sites or similar applications that make heavy use of faceted search is resource-intensive on the server side. A moderately busy site can keep a server tied up serving search information back to users.
Elasticsearch has built-in support for scaling it across multiple servers, both to expand capacity and provide fail-safe redundancy. It does this by using shards, a way of splitting data up and providing data integrity (a single source of truth) and redundancy (distributed on many machines).
Benefits of Elasticsearch for content marketers
Content marketers can leverage the power of Elasticsearch to get more out of specific marketing campaigns and existing content.
1. Quick searches
Loading time is a critical aspect of the user experience, and that includes the time spent searching. With Elasticsearch, searches through extensive website content are quick and present accurate info with little effort, allowing visitors to conduct their business quickly.
2. Data visualization
Kibana is a data visualization software that provides a browser-based interface to sift through Elasticsearch data. This enables you to create visualizations of the information that is queried and produce nice reports. These visualizations can then be placed into a custom interactive dashboard that makes finding patterns and details within the data much more straightforward.
3. Error corrections
How often have you misspelled a search query, yet a search engine still knows what you wanted to find? Elasticsearch allows site visitors to make spelling mistakes and still find the information they were looking for.
4. Alternative searches
With autocorrect, you can suggest alternative searches based on the previous search. Suggested terms and categories will be displayed that match the search intent of the site visitor.
5. Real-time analytics
Elasticsearch allows you to build real-time analytics that can provide unique customer insights such as customer visit patterns and more.
Benefits of Elasticsearch for eCommerce
Elasticsearch isn’t just for blogs and web applications; eCommerce sites can get enormous benefits as well.
1. Streamlining product catalogs
Elasticsearch makes it easy for you to add more functionality that streamlines your product catalogs. There is increased simplicity when building filters, facets, and aggregations on your product catalog to help users narrow down broader categories to find what they’re looking for.
2. Quick response times
Search engines need to move through a lot of information to find exactly what the customer is looking for. This complexity increases when there are products with a range of features of add ons as well. With Elasticsearch, you can gain faster response times for product queries and complex queries around product features.
3. Distributed searches
All crawling, data mining, querying, and indexing are carried out on a central server in a centralized search system. Elasticsearch, on the other hand, utilizes a distributed system that gives you the ability to have your searches distributed across systems or clusters, so access is quick, results are faster, and uptime is maintained.
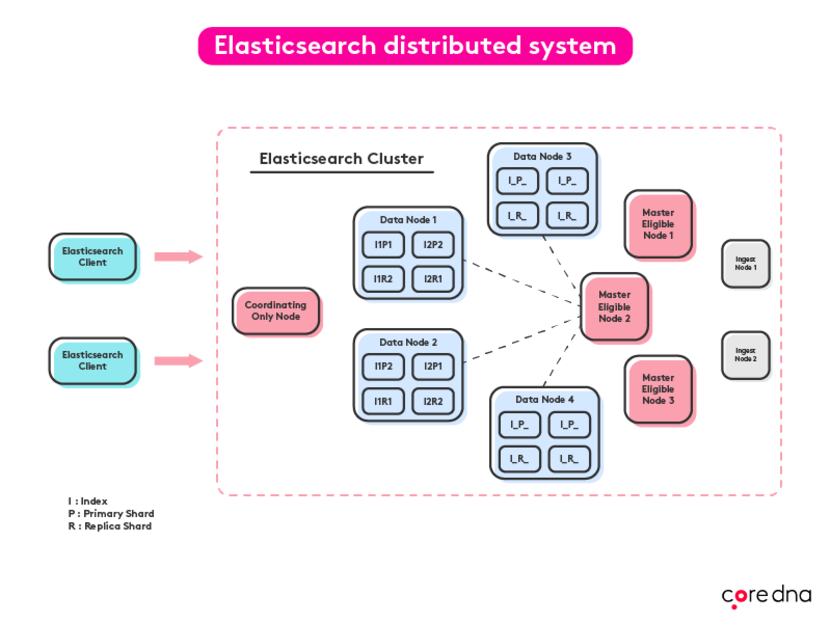
4. Real-time updates
Documents in Elasticsearch are stored in near real-time. This means that if a product entry is added or removed, such as updating your system or if the last piece of inventory was removed, changes are automatically detected and reflected in the search results.
5. Geo-localization
Elasticsearch enables you to store data related to latitude and longitude in a document. This provides the ability to make geo-localized searches for product information specific to your region.
6. Varied access points
Elasticsearch gives you the ability to provide different ways to access product catalogs using the browser, search, autocomplete incorrect terms, fuzzy search or direct access via a query. These options improve the opportunities for you to get your eCommerce product catalog in front of potential customers rather than returning errors when searching.
7. Improved customer conversions
The varied access points provided by Elasticsearch make it easier for users to find products which can lead to increased conversions. Rather than having to click or browse through an extensive catalog to find one item or closely related items, Elasticsearch can show the items a visitor is searching for with just a few clicks.
8. Connected digital experience
Elasticsearch can connect different aspects of the product catalog and other parts of the CMS to create a more engaging experience. For example, you can connect product info with an FAQ page or additional help info and a blog and then present it on one page as a product details page.
Elasticsearch real-life case studies
Here are some examples of what’s possible with Elasticsearch.
1. Flexible browsing
What is it: Flexible browsing gives you the ability to create searchable categories (categories that can be browsed) that relate to a search term within Elasticsearch.
Example: Elasticsearch can be used to go up and down the catalog categories in real-time.
Benefit: Categories are produced quickly but all categories aren’t displayed at once, only the relevant ones. This ensures that browsing is quick and isn’t a drain on resources.
2. Advanced searches
What is it: Advanced searching means that you can search for more than just a category, product name or product type. Searches can be broken down into more subcategories that narrow down and give more defined searches.
Example: Searches based on brand, parts, or car model are possible with Elasticsearch.
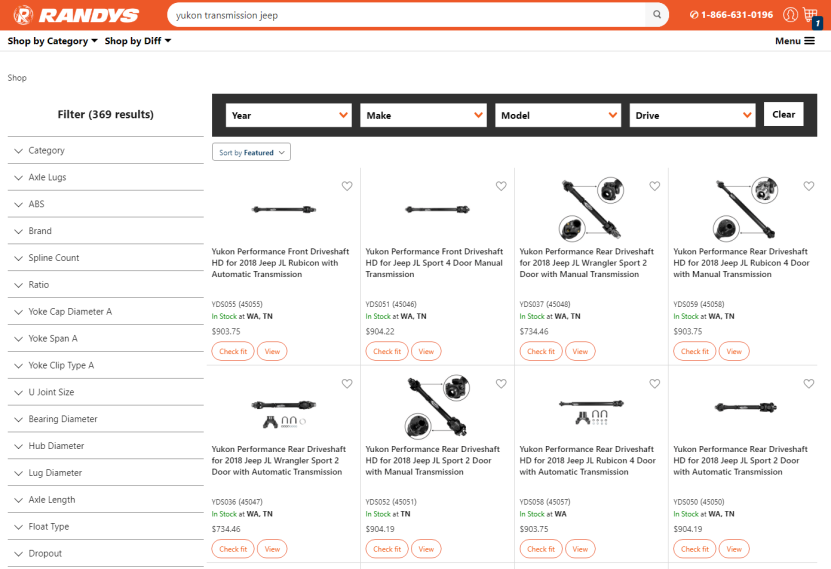
Benefit: It’s possible to find exactly what you’re looking for when you only have half of the information, and you’re able to narrow the search and support the search with the facet on the left.
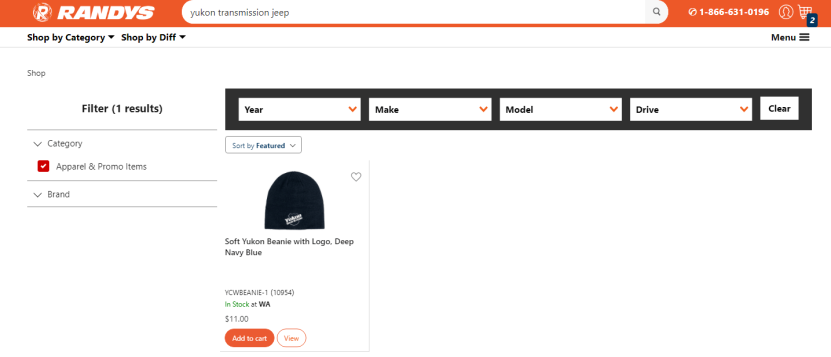
However, because of fuzzy logic, the search will also find things that weren’t intended. For example, JEEP and DEEP.
Go to Randy’s Worldwide and type in “Yukon transmission jeep”
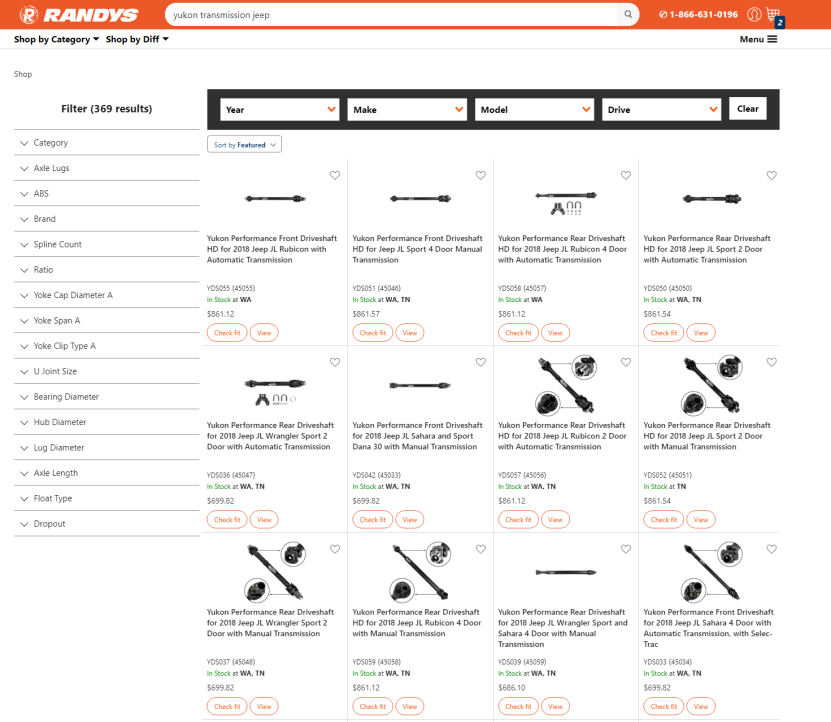
Then filter down the Category to “Apparel & Promo Items”
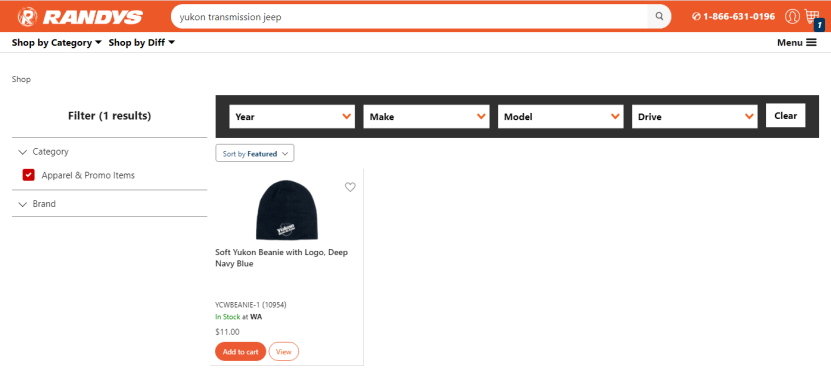
It’ll show “Soft Yukon Beanie with Logo, Deep Navy Blue” because it has the word “Yukon”, and “Deep”, and the system predicts that DEEP = JEEP
3. Faceted search
What is it: Faceted search provides a way to narrow down search results by applying filters.
Example: It grabs all the facets of the products and brings those in for the full search. It will only show the category of the products that are displayed. Hence the 369 results, not showing 10k results.
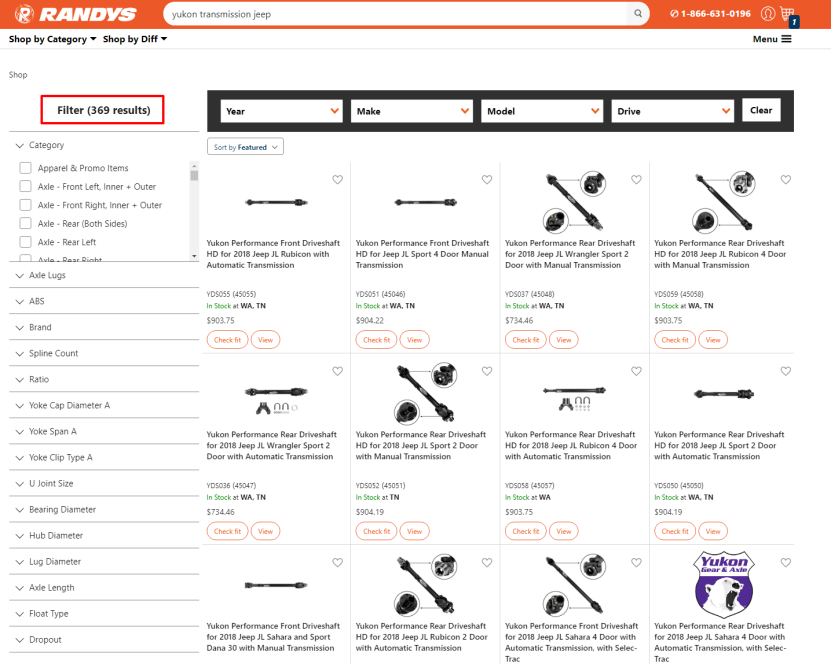
Benefit: It’s possible to use imperfect info to get a list of products, but Elasticsearch then builds up a list of facets with perfect information as if you searched correctly. Essentially, the search may think that you want 369 products, and the properties (Axle lugs, ratio, etc.) of those products are displayed.
It doesn’t matter how random the search is; it can be filtered further to a specific product you want. For example:
No one would expect you were looking for a beanie, but because of the facet, you’re able to narrow it down to a beanie by clicking on the category of apparel after you’ve searched.
So, rather than looking through an apparel section, you could type in a broad search and using the facet, you can quickly narrow the individual products.
4. Site search
What is it: Elasticsearch can record historical data about your previous searches on a site and then provide you with related searches the next time you search.
Example: We’re looking for “headless”, but Elasticsearch also pulls up related searches based on search history, page tags, text associated with said searches.
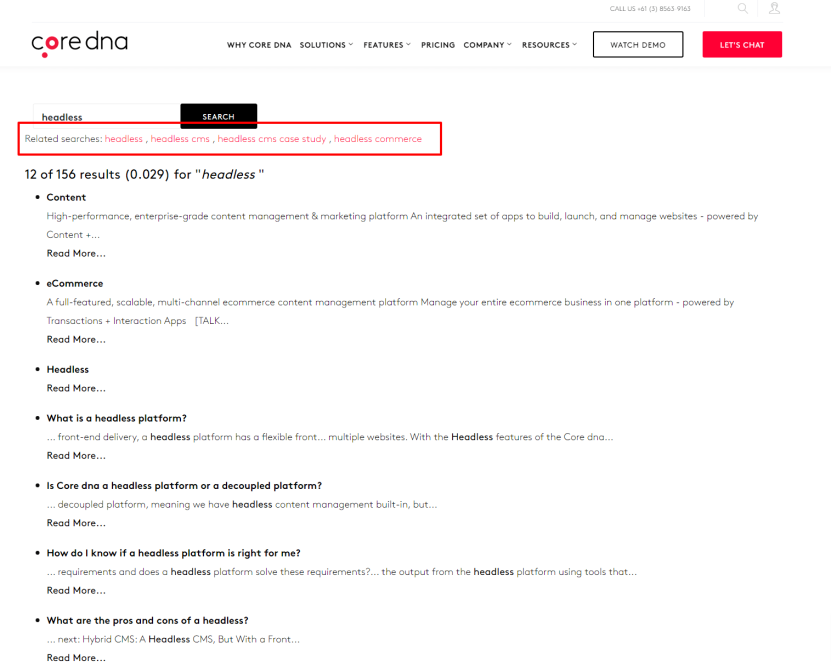
Benefits: This makes it easier for visitors to find the content they’re looking for because Elasticsearch understands the context with which they’re searching.
5. Content aggregation
What is it: An aggregated search adds more weighted importance to a particular search term. This helps you to narrow your search and achieve more exact matches.
Example: 463 is the number of aggregated products that fall under the price range of $0 to $49.
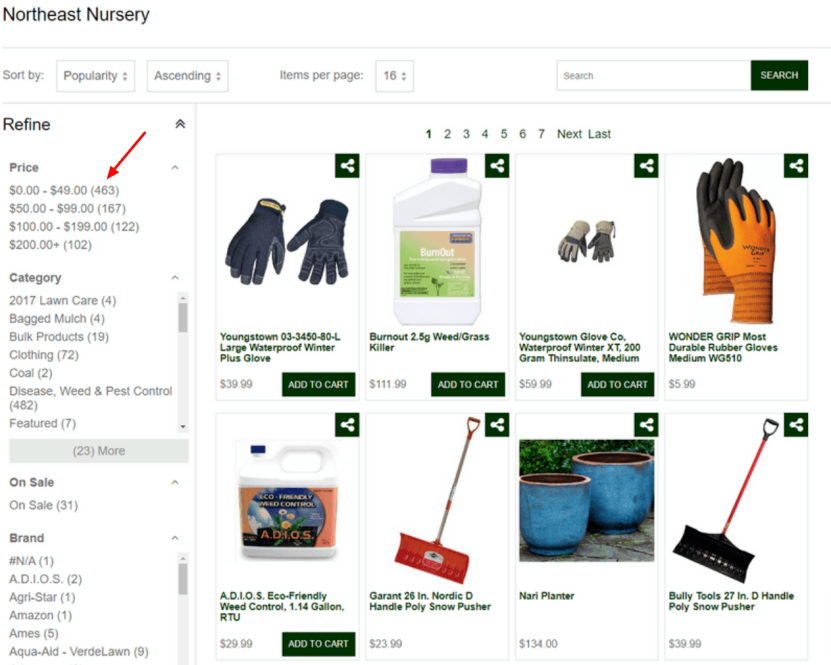
Content aggregation produces a faceted search with dynamic facets that can be created based on any properties of this product’s product or relationship.
It’s possible to narrow search results based on product names, descriptions, SKUs, and more by giving different weights to different fields.
Autocomplete and fuzzy search are also enabled with Elasticsearch and can provide results even with incomplete information. The search quality also improves as there are no identical pages in the search results, and results can be sorted based on relevance. Wildcard queries are also possible, which returns results that contain wildcard patterns or wildcard operators. Regex queries can be used to create complex patterns that can dig into the content. For example, finding someone’s name that starts with T and ends with Y.
Get more out of Elasticsearch with Core dna
Elasticsearch provides unique search functionality that can benefit developers, marketers and eCommerce store visitors alike. However, the search is only one aspect of the digital experience.
When combined with a headless digital experience platform like Core dna, you can provide your visitors with more than just great search results, but you can ensure the content they find when they’re searching is top quality as well.
Learn more about maximizing your eCommerce potential by reading: Multi-Vendor eCommerce Marketplace: The Definitive Guide.













