Internal Site Search Best Practices to Boost Conversions

Mastering internal site search can be the key to driving more conversions. By optimizing this often-overlooked feature, you can enhance the user experience and ensure your visitors find exactly what they need.
If you have ever typed in a search bar on a website for a product you are looking for, you are already familiar with site search. Site search is a feature on websites that enables users to search for specific content. It's quite a handy feature found in many different places, such as Amazon, Reddit, and many popular eCommerce websites.
With the growth of eCommerce and a general increase in demand for getting information quickly, site search is necessary to make your website as user-friendly as possible. The best user experience will drive website conversions. Site search allows users to find the answer to specific questions or help them find what they are looking for without resorting to Google.
In this article, we will discuss what site search is, how it benefits your business, how to get started with Google Analytics Site Search, and how it could potentially provide a competitive edge.
Key takeaways
- Site Search Importance: Site search is critical for enhancing user experience, increasing conversions, and helping customers find exactly what they need quickly on your website.
- Optimizing Site Search: Effective optimization reduces customer frustration, generates valuable data, and improves navigation, leading to better customer retention and increased sales.
- Google Analytics Integration: Tracking site search in Google Analytics provides insights into customer behavior, search terms, and page visits, allowing for optimization of content and user experience.
- Best Practices for Site Search: Key practices include visibility of the search bar, autocomplete functionality, mobile optimization, and the use of filters and facets for better search results.
On this page:
What Is Site Search?
Site search is a feature offered by many websites and search engines that allows users to quickly and effectively find specific content within the website. For example, you can use site search to find items, people, places, or topics. Site search is usually specifically tailored to the website. It ensures that the most recent content is available by continuously indexing the site.
In addition to providing you with the list of results from your search, it will also provide links that will take you directly to the pages where your keywords are located. Thus, site search allows users to easily connect with the material they need while also collecting valuable information about the content and items they are most interested in.
Site search is often more precise than using a general web search engine such as Google or Yahoo. In addition, by helping visitors explore the site, site search opens opportunities to discover content on the website that the user may not have known was available or may not have realized they were interested in.

Why Should You Optimise Your Site Search?
Simply said, if site search isn't implemented appropriately, then visitors can't discover what they're searching for on your website, which means they're unlikely to convert. Similarly, customers who can't locate answers might create expensive support requests and calls. Both of these situations result in lost time, sales, leads, and profit.
On the other hand, great use of site search can make your brand image stronger and your website easier to navigate and use. With a great experience, your customers are more likely to subscribe to newsletters, spread the word about your business, and become repeat customers.
Let's go over some of the other benefits of optimising your site search.
Creates More Efficient Experiences for Customers
Customers are more likely to do business with you if they can easily browse your website, search for the product they have in mind, and instantly receive an appropriate response. Site search makes this happen by pulling a list of relevant results based on the customer's inquiry and allowing them to go to a particular page immediately. This will lead to conversion and prevent customers from becoming frustrated and leaving due to unsuccessful search efforts.
Provides You Valuable Data About Customers
The only people who tell you exactly what they're looking for in their own words are site searchers. This information gives you an idea of what customers are searching for when they search for your products and allows you to further optimize your site based on the keywords used. This data could be used to prioritize relevancy and reduce the time users spent searching through results.
Furthermore, you may find that users are searching for content that you don't have on your site yet, which allows you to fill in the blanks and post relative content. Lastly, site search analytics can help you better understand your customer by providing you with information about exactly who they are. It can also provide insight into what products are more prevalent at certain times.
Helps Your Reach Your Most Valuable Customers
Most site searchers already know the product they are looking for, are already familiar with your brand, and are on a mission to buy that product. According to eConsultancy, 15% of visitors to a website use the search tool, but contribute to 45% of income. Users who search are also 1.8 times more likely to convert than those who do not. So, it’s important to cater to these customers and provide a great experience.
By creating a fast, easy, and efficient experience for these customers, you can provide the customer with exactly what they are looking for, possibly create a long-term relationship with the customer, and increase conversions.
Helps You with Site Scalability
As a business grows, so does the number of products or content on the website. Unfortunately, more website content can easily lead to a poor user experience if the appropriate steps are not taken. With a significantly growing website, it can be nearly impossible for users to find exactly what they are looking for without site search. With optimised site search, users will still be able to find what they are looking for and discover related content or products despite the website growing significantly.
Helps Customer Solve Issues Quickly with Little Intervention
Customers prefer to solve their own issues without reaching out to support or sending in support tickets. According to Parature, 84% of customers would prefer to use search engines to find a solution to a problem on their own.
Good site search practices improve your customer service skills by increasing your visitors' ability to discover solutions to their problems. The most essential component of effective customer service, according to 41% of consumers, is getting concerns handled fast. Your consumers may accomplish precisely that with optimised site search. In the long run, not handling support tickets and frustrated customers will save your company time and money.
How to Set up Internal Site Search in Google Analytics
Now that you have a better idea of what site search is and why you should use it and optimise it for your business website, let's go over Google Analytics site search tracking. With Google Analytics Site Search, you can see the search keywords customers use, which pages they start their search on, and the pages they visit based on the search results page. This information provides insight into your website content, navigation setup, and your search campaigns.
Before you can use the reports, you must first configure site search in Google Analytics. Let's go over how you can configure your website to get these reports:
Search Query and Category Parameters
Finding the query parameter that powers your site's search feature is the simplest method to configure the site search reports.
Begin by conducting a search on your website and inspecting the URL for the search results page. If you search the word “contact” and your search function accepts query parameters, you'll get a URL that looks something like one of these:
- examplewebsite.com/search?q=contact
- examplewebsite.com/index.php?id=search&term=contact
- examplewebsite.com/search.asp?search_term=contact&id=ac9024
Suppose the URL doesn't have a question mark, an ampersand, or the word that you searched ("contact" in this case). Then, you will want to use a different approach rather than the query and category parameter approach. However, if it does look like this, continue through to the following steps:
Step 1: Identify the query parameter.
To identify the query parameter, look for the term you just searched. Before that, there should be an equal sign. Before the equal sign, you will see a character or word. Then, in front of that, you will see a question mark or ampersand. The query parameter is whatever is between the question mark or ampersand and the equals sign.
- In example 1, “q” is the query parameter.
- In example 2, “term” is the query parameter.
- In example 3, “search_term” is the query parameter.
Step 2: Configure Google Analytics.
Navigate to the 'Admin' area of your Google Analytics account. Then, click the 'View Settings' option.
Step 3: Change site search settings.
Set ‘Site Search Tracking' to ‘On' and enter your query parameter in the 'Site Search Settings.' Google Analytics allows you to specify up to five query parameters separated by commas.
If you select 'Strip query parameters from URL,' your search will be hidden from your reports. However, you'll see rows in your content reports for each individual search phrase used, such as '/search?q=contact' if you select this option.
Make sure to save your settings.
Step 4: Test it out.
To make sure your site search analytics are working:
- Perform a few searches on your site, then wait at least 10 minutes.
- Set your date range to 'today' in the Google Analytics view (where you changed your settings).
- Navigate to Behaviour, Site Search, then Search Terms Report.
If you see data there, then congratulations, that means your site search is working. If your site uses categories, then navigate to the ‘Site Search Category’ link to view that data.
Final Note about categories using this method:
Site Search also enables categorizing. If users can filter search results or search inside certain website areas, you should use this option. First, you'll need to identify the search parameter used to refine the results. Then, using the same method as before, you can determine the query parameter used for the search term. This option can be left off if your search engine doesn't have categories or if you don’t need it.
GET Based Search Engine
Your internal site search engine can also use a GET based method. If your site sends users’ search information to your web server via the URL, then you are using a GET based search engine.
Follow the same steps as above (in the ‘Search Query and Category Parameters’ section) to set up, view, and test your Google Analytics Site Search data using a GET based engine.
POST Based Search Engine
If your site sends users’ search information to your web server via the HTTP request and not the URL, then you are using a POST based search engine. Since the search is not sent via the URL, the search term and query parameters do not appear in the URL like the previous two methods.
Google recommends two methods to set up Google Analytic search tracking if you are using the POST method.
Method 1: Convert your POST based search engine to a GET based search engine.
The POST method is not the ideal method for internal site searches. Using the GET based search engine is better for website optimization. So, the recommended approach is to convert your POST based search engine to a GET based search engine. Afterward, review the 'GET Based Search Engine' section in this article to set up Google Analytics search tracking.
Method 2: Whenever a search is performed, send virtual pageviews.
If you cannot convert the POST based search engine, you can select to have virtual pageviews sent whenever a search is performed. Code would need to be written to identify and extract the search term then append the query parameter to it before the pageview is sent to Google Analytics. By doing this, the search query parameter and search term are appended to the URL.
Once you have it set up, you can configure your site search settings in Google Analytics reporting view. In this case, you would turn ‘Site Search Tracking’ on and enter your query parameter.

Best Practices for Site Search
Merely providing site search is insufficient — you must provide clients with a high-quality search experience or risk losing them. According to Forrester, up to 68% of customers would abandon a site that delivered a bad search experience. So, it’s essential to use site search as efficiently as possible. Here are a few best practice tips:
- The search bar should be visible and easy to find.
- Utilize auto-complete.
- On the internal search results page, bold the search query keywords.
- Optimise for mobile and voice searches.
- Provide searchers with abundant filtering options.
- Flexible browsing: go up and down the catalogue categories in real-time.
- Advanced searches: Allow users to search for more than just a category, product name, or product type. Allow searches to be broken down into more subcategories that narrow down and give more defined information.
- Faceted searches: Narrow down search results by applying filters.
- Content aggregation: An aggregated search adds more weighted importance to a particular search term. This helps you to narrow your search and achieve more exact matches.
- Avoid a "no-results page."
- Leave the search terms in the search box.
- Make sure your site search is tolerant of typos.
- Don't optimise for industry jargon, optimise for the terms your customers use instead.
- Provide search access to things other than your products: Example, SKUs, category, etc.
- Consider adding graphics and Add-to-Cart buttons to search results.
- Don't be afraid to suggest complementary items or offer upgrades.
- Deliver search results quickly.
- Control crawl budget by using parameter-based on-site search URLs.
- Avoid potential duplicate content with URL redirects.
- Avoid thin content issues by handling 'No Result' pages.
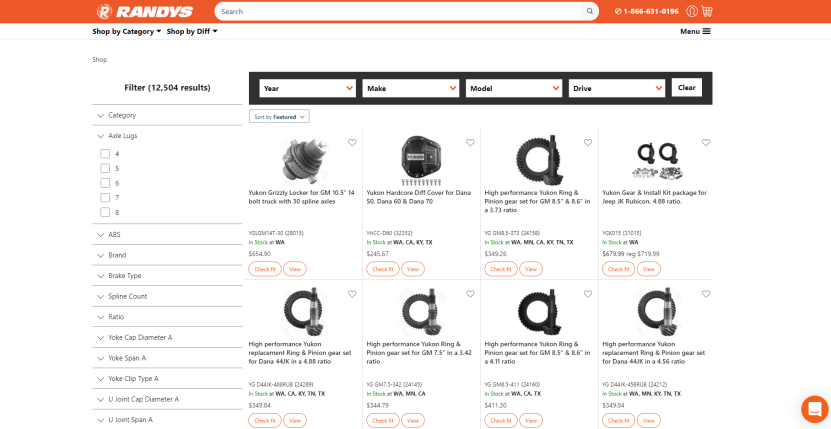
As you can see from the images above, we chose to provide three different search options for the different personas on the Randy's Worldwide website.
- Basic user: There are two types of broad category searches with real-time updates. The results are organised based on key product characteristics.
- DIY user: There is a predictive search with fuzzy logic and facets for quick selection.
- Experienced user: There is a product code/SKU search for quick cart and order creation.
Furthermore, connecting site search events to analytics provides invaluable information for understanding the behaviour of product searchers. Site search provides the ability to connect a search with an outcome and gain insights into the customer’s intent. This information can be used to drive marketing and product development. Core DNA uses the flexibility and customization provided by Elasticsearch to provide these services and the valuable information that comes with it.
Wrapping Up Site Search
Site search is one of the best ways to control the customer experience on your website. It has the potential to generate conversion by making your site easy and efficient to navigate while benefiting your business in several other ways. Using the best practice tips and site search tools in this article will help you make your website user-friendly for your customers.
If you use the Core DNA platform, then you will have support in implementing and optimising your site search to create the best experience for your users. The Core dna development team releases new updates and features to the platform every two weeks - being a SaaS system, all customers get access to these great features and regular platform improvements.













